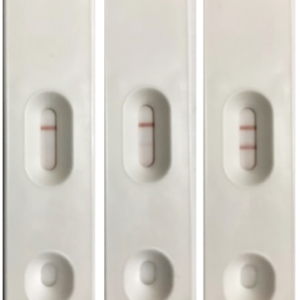
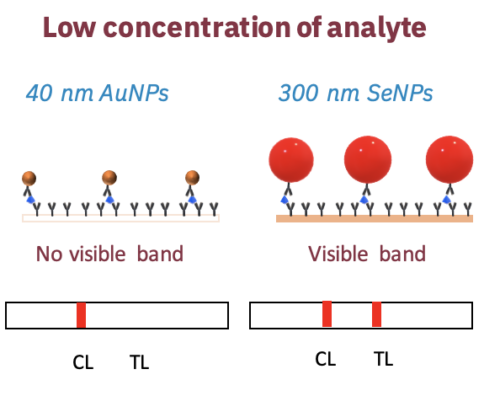
Glantreo’s highly monodispersed Selenium Nanoparticles (SeNP) are available in a number of sizes including, 80, 150, 250 and 300 nm diameters. Absorbance wavelengths of the 2 larger SeNPs have lambda max. values at 577 nm and 640 nm respectively. Absorbance at these wavelengths gives the SeNPs a strong red colour, which along with their compatibility for passive protein conjugation, makes them ideal candidates for biological labelling applications, including lateral flow assays (LFA). Furthermore, the intrinsic fluorescence properties of Selenium nanoparticles allow them to be used in imaging applications. Finally, the anti-cancer, anti-bacteria and anti-fungal properties of selenium nanoparticles combined with their biological labelling properties place them in a unique position as a self-reporting therapeutic.
Quantities Available – 5ml packs to >100 litre per month contracted
❖Lateral flow assays
❖Labelling and monitoring molecules
❖Anti-microbial additive
❖Supplement for animal feed
❖Additive in fertiliser
❖Anti-cancer and therapy delivery vehicle
❖Solar cells
See link to paper below under Product Data and References for more in-depth review.


| Particle Diameter | 80nm | 150nm | 250nm | 300nm |
| Λmax (nm) | 288 +/- 10 | 508 +/- 10 | 577 +/-10 | 640 +/- 10 |
| Theoretical Λmax as predicted by Mie Scattering (nm) | 288 | 508 | 577 | 640 |
| Optical Density (OD) | 19-21 | 19-21 | 19-21 | 19-21 |
| pH | 4.5-7 | 4.5-7 | 4.5-7 | 4.5-7 |
| Presentation matrix | Water | Water | Water | Water |
| Shelf life | >12 months | >12 months | >12 months | >12 months |
| Storage | 2-8 degrees Celsius | 2-8 degrees Celsius | 2-8 degrees Celsius | 2-8 degrees Celsius |
| Pack size | 5ml to multi litre | 5ml to multi litre | 5ml to multi litre | 5ml to multi litre |
| 80nm & 150nm diameter particles available in wt% of 0.01%, 0.15% as dispersions in water | ||||
If you have published and cited Glantreo’s materials then click here to let us know.
Clifford A. Barnes, Andreas Elsaesser, Joanna Arkusz, Anna Smok, Jadwiga Palus, Anna Lesniak, Anna Salvati, John P. Hanrahan, Wim H. de Jong, Elzbieta Dziubaltowska, Maciej St?pnik, Konrad Rydzynski, George McKerr, Iseult Lynch, Kenneth A. Dawson and C. Vyvyan Howard, Reproducible Comet Assay of Amorphous Silica Nanoparticles Detects No Genotoxicity. Nano Letters, 2008, 8 (9), pp 3069–3074. doi: 10.1021/nl801661w http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/nl801661w#citing
Makoto Ema∗, Norihiro Kobayashi, Masato Naya, Sosuke Hanai, Junko Nakanishi, Reproductive and developmental toxicity studies of manufactured nanomaterials, Reproductive Toxicology 30 (2010) 343–352
Iseult Lynch, Sara Linse, C Vyvyan Howard, Maciej Stepnik, Konrad Rydzynski, John Hanrahan, Wim de Jong, Dominique Langevin, Joachim Rädler, Wolfgang Parak, Yuri Volkov, Marek Radomski, Robert Thomas, Jacob Klein, Andrew A Barron, Colin Janssen, Fiona M Lyons, Francis Quinn, Bert Swennen, Peter Cuypers, Angela Duffy and Kenneth A Dawson, NANOINTERACT: A rational approach to the interaction between nanoscale materials and living matter, Journal of Physics: Conference Series Volume 170 Number 1.doi:10.1088/1742-6596/170/1/012040 http://iopscience.iop.org/1742-6596/170/1/012040/cites
Bashir Mustafa Mohamed, Navin Kumar Verma, Adriele Prina-Mello, Yvonne Williams, Anthony M Davies, Gabor Bakos, Laragh Tormey, Connla Edwards, John Hanrahan, Anna Salvati, Iseult Lynch, Kenneth Dawson, Dermot Kelleher,and Yuri Volkov, Activation of stress-related signalling pathway in human cells upon SiO2 nanoparticles exposure as an early indicator of cytotoxicity. Journal of Nanobiotechnology. 2011;9:29. doi:10.1186/1477-3155-9-29.http://www.jnanobiotechnology.com/content/9/1/29
Margriet V.D.Z. Park a,b,⁎, Wijtske Annema a, Anna Salvati c, Anna Lesniak c, Andreas Elsaesser d, Clifford Barnes d, George McKerr d, C. Vyvyan Howard d, Iseult Lynch c, Kenneth A. Dawson c, Aldert H. Piersma a,e, Wim H. de Jong a, In vitro developmental toxicity test detects inhibition of stem cell differentiation by silica nanoparticles, Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 240 (2009) 108–116
Markus Roller, In vitro genotoxicity data of nanomaterials compared to carcinogenic potency of inorganic substances after inhalational exposure, Mutation Research 727 (2011) 72–85
Mostafa Yazdimamaghani, PhDa,b, Philip J. Moos, PhDb,c, Marina A. Dobrovolskaia, PhDd, Hamidreza Ghandehari, PhD, Genotoxicity of amorphous silica nanoparticles: Status and prospects, Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine 16 (2019) 106–125