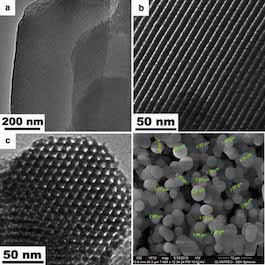
Mesostructured cellular foam (MCF) is a type of mesoporous silica with large pore sizes (100nm) and a continuous 3D pore system. The material is hydrothermally robust and able to withstand the high temperatures and pressures required for modifications that transform MCF silica into catalysts, biocatalysts and adsorbents. Due to its large porous network, MCF has a higher loading capacity, lower diffusional restriction and better stability than MCM-41 or SBA-15. These characteristics are preferable for any applications that involve bulky molecules, high temperatures or harsh conditions, such as hydrogenation, heck coupling, glucose conversion, CO2 capture, etc. Glantreo has vast knowledge in the manufacture of Mesoporous Silica (MS). For almost 15 years we have supplied large quantities (up to kg quantites) of Mesoporous Silica to our Researcher and Industry partners.



The large pore structures present in MCF enable it to act as a scaffold to incorporate active sites for catalytic applications. Active sites such as metal oxides and nanoparticles enhance catalysis for chemical reactions, while the addition of functional groups to MCF can be used to immobilise and orient enzymes to enhance enzymatic reactions:
❖ Catalysis: MCF can be used as a catalyst support for various reactions, such as hydrogenation of phenylacetylene and heck coupling reaction of arylboronic acid.
❖ Biocatalysis: MCF can be used as a biocatalyst support for various enzymatic reactions, such as conversion of glucose to gluconic acid and hydrolysis of casein.
❖ Adsorption: MCF can be used as an adsorbent for various separation processes, such as CO2 capture and adsorption of L-tryptophan.
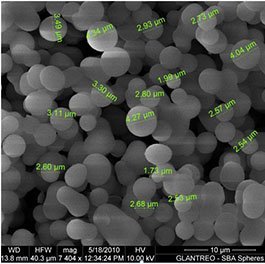
| Mean Particle Size dv50 (um) | <2.5um |
| Pore Diameter (nm) | 15.0-25.0 |
| Surface Area (m2g-1) | 350-550 |
| Total Pore Volume (cm3g-1) | 1.5-3.0 |
| Mesopore Volume (cm3g-1) | 1.5-3.0 |
| Chemistry | Raw Silica |
| Pack Size | 5g, 10g |
Below you will find the different Product variations in our MCF range. In order to make them easy to find we have added a search function. To narrow down your selection you can search within a table.
| Product Code | Particle Size | Pore size | Pack size | Functionlaition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCF0.11000R-5 | <2.5um | 150A-250A | 5g | Raw Silica |
| MCF0.11000R-10 | <2.5um | 150A-250A | 10g | Raw Silica |
If you have published and cited Glantreo’s materials then click here to let us know.
Noreldeen H. Abdallah, Miriam Schlumpberger, Darragh A. Gaffney, John P. Hanrahan, Joseph M. Tobin, Edmond Magner, Comparison of mesoporous silicate supports for the immobilisation and activity of cytochrome c and lipase, Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, Volume 108, October 2014, Pages 82-88, ISSN 1381-1177http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1381117714001805
Robert J. Ahern, John P. Hanrahan, Joseph M. Tobin, Katie B. Ryan, Abina M. Crean, Comparison of fenofibrate–mesoporous silica drug-loading processes for enhanced drug delivery, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 50 (2013) 400–409
Robert J. Ahern, John P. Hanrahan, Joseph M. Tobin, Katie B. Ryan, Abina M. Crean, Comparison of fenofibrate–mesoporous silica drug-loading processes for enhanced drug delivery, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Volume 50, Issues 3–4, 20 November 2013, Pages 400-409, ISSN 0928-0987 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928098713003400
Davide Barreca, Mark P. Copley, Andrew E. Graham, Justin D. Holmes, Michael A. Morris, Roberta Seraglia, Trevor R. Spalding, Eugenio Tondello, Methanolysis of styrene oxide catalysed by a highly efficient zirconium-doped mesoporous silica, Applied Catalysis A: General, Volume 304, 10 May 2006, Pages 14-20, ISSN 0926-860Xhttp://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926860X06001013
Paul Delaney, Healy RM, Hanrahan JP, Gibson LT, Wenger JC, Morris MA, Holmes JD. Porous silica spheres as indoor air pollutant scavengers. Journal of Environmental Monitoring. 2010 Dec;12(12):2244-51. doi: 10.1039/c0em00226g.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20941430
Tahnee J. Deninga,1, Dmitry Zemlyanovb, Lynne S. Taylora, Application of an adsorption isotherm to explain incomplete drug release from ordered mesoporous silica materials under supersaturating conditions, Journal of Controlled Release 307 (2019) 186–199
Jessica Fordea, Alex Vakurovb, Tim D. Gibsonb, Paul Millnerb, Mícheál Whelehana, Ian W. Marisona, Ciarán Ó’Fágáina, Chemical modification and immobilisation of lipase B from Candida antarctica onto mesoporous silicates, Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic 66 (2010) 203–209
Tomer Lapidot, Omar K. Matar, Jerry Y.Y. Heng, Calcium sulphate crystallisation in the presence of mesoporous silica particles: Experiments and population balance modelling, Chemical Engineering Science 202 (2019) 238–249
Carol A. McCarthy, Waleed Faisal, Joseph P. O’Shea, Colm Murphy, Robert J. Aherne, Katie B. Ryan, Brendan T. Griffin, Abina M. Crean , In vitro dissolution models for the prediction of in vivo performance of an oral mesoporous silica formulation, Journal of Controlled Release, Volume 250, 28 March 2017, Pages 86-95
K. Lamb, R.A. Mole, D. Yu, R. de Marco, J.R. Bartlett, S. Windsor, S.P. Jiang, J. Zhang, V.K. Peterson, Proton dynamics in phosphotungstic acid impregnated mesoporous silica proton exchange membrane materials, Green Energy & Environment (2017), doi: 10.1016/ j.gee.2017.06.007.
Mareike Siebert∗, Thorben Detering, Ralf G. Berger, An immobilized fungal chlorogenase rapidly degrades chlorogenic acid in a T coffee beverage without altering its sensory properties, LWT – Food Science and Technology 115 (2019) 108426
Sugata P. Tan*, Elizabeth Barsotti, Mohammad Piri, Application of material balance for the phase transition of fluid mixtures confined in nanopores, Fluid Phase Equilibria 496 (2019) 31e41
Laura J. Waters a,⇑, Talib Hussain a, Gareth Parkes a, John P. Hanrahan b, Joseph M. Tobin, Inclusion of fenofibrate in a series of mesoporous silicas using microwave irradiation, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 85 (2013) 936–941
Laura J. Waters, Talib Hussain, Gareth Parkes, John P. Hanrahan, Joseph M. Tobin, Inclusion of fenofibrate in a series of mesoporous silicas using microwave irradiation, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, Volume 85, Issue 3, Part B, November 2013, Pages 936-941, ISSN 0939-6411http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0939641113002816

Notifications